Pipe is a hollow
structure designed to provide an enclosed pathway for fluids to flow, usually
manufactured from cast metal or plastic. This section discusses some common methods for joining pipes and pipe ends with instruments together.
manufactured from cast metal or plastic. This section discusses some common methods for joining pipes and pipe ends with instruments together.
Tapered thread pipe
fittings
·
Thread fittings are more preferred for
smaller pipe sizes.
·
A very common design of threaded pipe
fitting is the tapered pipe thread design.
·
The intent of a tapered thread is to
allow the pipe and fitting to “wedge” together when engaged, creating a joint
that is both mechanically rugged and leak-free.
Several different
standards exist for tapered-thread pipe fittings. For each standard, the angle
of
the thread is fixed, as is the angle of taper. Thread pitch (the number of threads per unit length) varies with the diameter of pipe fitting.
the thread is fixed, as is the angle of taper. Thread pitch (the number of threads per unit length) varies with the diameter of pipe fitting.
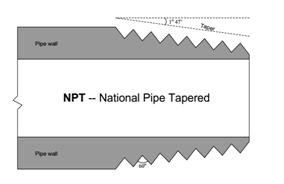
The most common tapered
thread standard for general-purpose piping is the NPT, or National Pipe Taper
design. NPT threads have an angle of 60° and a taper of 1°47’.
NPT pipe threads must
have some form of sealant applied prior to assembly to ensure pressure tight
sealing between the threads. Teflon tape and various liquid pipe “dope”
compounds work well for this purpose. Sealants are necessary with NPT threads
for two reasons: to lubricate the male and female pieces (to guard against
galling the metal surfaces), and also to fill the spiral gap formed between the
root of the female thread and the crest of the male thread.
Another tapered-thread standard is the BSPR, or British Standard Pipe Tapered. BSPT threads have a narrower thread angle than NPT threads (55° instead of 60°) but the same taper angle 1°47’.
Parallel-thread
pipe fittings
·
One popular parallel-thread pipe
standard is the BSPP, or British Standard Pipe Parallel.
·
Like the BSPT (tapered) standard, the
thread angle of BSPP is 55°.
·
Sealing is accomplished by means of an
O-ring which compresses against the shoulder of the matching female fitting:





No comments:
Post a Comment